Abstract
Background: As a single agent, rituximab produces an overall response rate (ORR) of 20-50% in patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL). Acquired resistance occurs however, due, in part to defective host immune effector mechanisms. Efforts to augment immune function have included combining rituximab with immune modulators, e.g. IL-2, IL-12, interferon,and lenalidomide, which has resulted in improved response rates. CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell responses and Ipilimumab is a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4, CD152) expressed on activated T cells. Ipilimumab disrupts the interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligands, B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86); thus augmenting the T cell activation. We therefore hypothesized that ipilimumab would augment the efficacy of rituximab.
Methods: Patients ≥ 18 years old with r/r CD20+ NHL, measurable disease, KPS ≥ 70%, neutrophils ≥ 1000/mm3, platelets ≥ 50,000/mm3, and adequate kidney and liver function were eligible. In this phase I study with an expansion cohort, after establishing the recommended Phase II dose (RP2D), study patients would be randomized to differing treatment schedules of rituximab and ipilimumab to better assess the effects on rituximab-mediated cytotoxicity. As induction in the phase I component, ipilimumab was administered every 3 weeks for 4 doses and rituximab given every week for four weeks. Primary endpoints included: toxicity and determination of the maximum tolerated dose (MTD)/RP2D during the first 7 weeks of induction with ipilimumab (2 doses) when given in combination with rituximab (4 doses, 375mg/m2 per dose). Secondary end points included biomarkers of immune response, ORR, progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). In the phase I component a standard 3+3 design was used to determine the MTD/RP2D. After the RP2D was established, 20 more patients were randomized to one of two schedules: on Arm A, ipilimumab on Day 1 with rituximab, and on Arm B, rituximab day 1 and ipilimumab delayed until Day 15 to assess the ability of ipilimumab to augment the rituximab-mediated B cell depletion (a surrogate biomarker for ipilimumab-mediated augmentation of rituxan targeted ADCC). After induction in both the Phase I and the expansion cohorts, maintenance ipilimumab and rituximab were given every 12 weeks (+/- 1 week) on the same day for 1 year. Immune correlates included assessment of 16 serum cytokines using multiplex assays, and T cell subset and immunophenotypic analysis by flow cytometry.
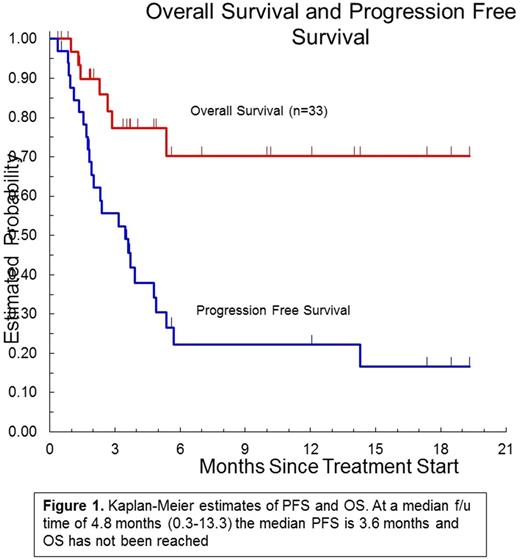
Results : As of August 1 2017, planned accrual was completed with 33 patients enrolled (2 small lymphocytic lymphoma, 13 follicular lymphoma, 7 diffuse large B cell lymphoma, 2 mantle cell lymphomaL, 9 indeterminate): 26 are assessable for toxicity at 7 weeks. The median age was 62 (32-77) and the median number of prior regimens was 3 (1-6). The RP2D of ipilimumab is 3 mg/kg, which was the highest dose tested when given with rituximab (375mg/m2). The most common grade 1-2 AEs (≥ 20%) were: anemia (21%), fatigue (33%), AST elevated (24%), low albumin (24%), elevated alkaline phosphatase (21%), edema limbs (21%), rash maculo-papular (21%). The most common grade 3-4 AEs (≥ 5%) were: lymphocytopenia (18%), anemia (12%), diarrhea (12%), leukopenia neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hypokalemia, rash maculo-papular, and hyponatremia 9% each. There were no treatment-related deaths. Twenty-seven patients were evaluable for response; 12 had progressive disease, 7 stable disease, 6 partial response and 2 complete response for an overall response rate of 30%. Responses were observed in 6 of 11 evaluable FL patients (ORR 54%). At a median follow-up time of 4.8 months, the median PFS is 3.4 months and the median OS has not been reached (Figure 1). Serum cytokine analysis revealed elevated levels of IL-2, TNF-α, and GM-CSFpredicted response (p ≤ 0.05). B cell depletion, phenotypic and T cell subset analysis is ongoing.
Conclusion: The RP2D of ipilimumab when given in combination with rituximab is 3 mg/kg and at this dose it is safe and moderately well tolerated. Efficacy is modest in this heavily pretreated patient population however more promising in FL patients with several patients having durable remissions. Immune correlative analysis has thus far potentially identified several cytokines that may predict response
Tuscano: Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Ailawadhi: Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Chen: Affimed: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Jonas: AbbVie, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Pharmacyclics, Genentech/Roche, Glycomimetics, Esanex, Kalobios: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rigel: Consultancy. Wun: Pfizer: Other: Steering Committee: RESET study, Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Steering Committee for Cassini Study and Callisto Program, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal